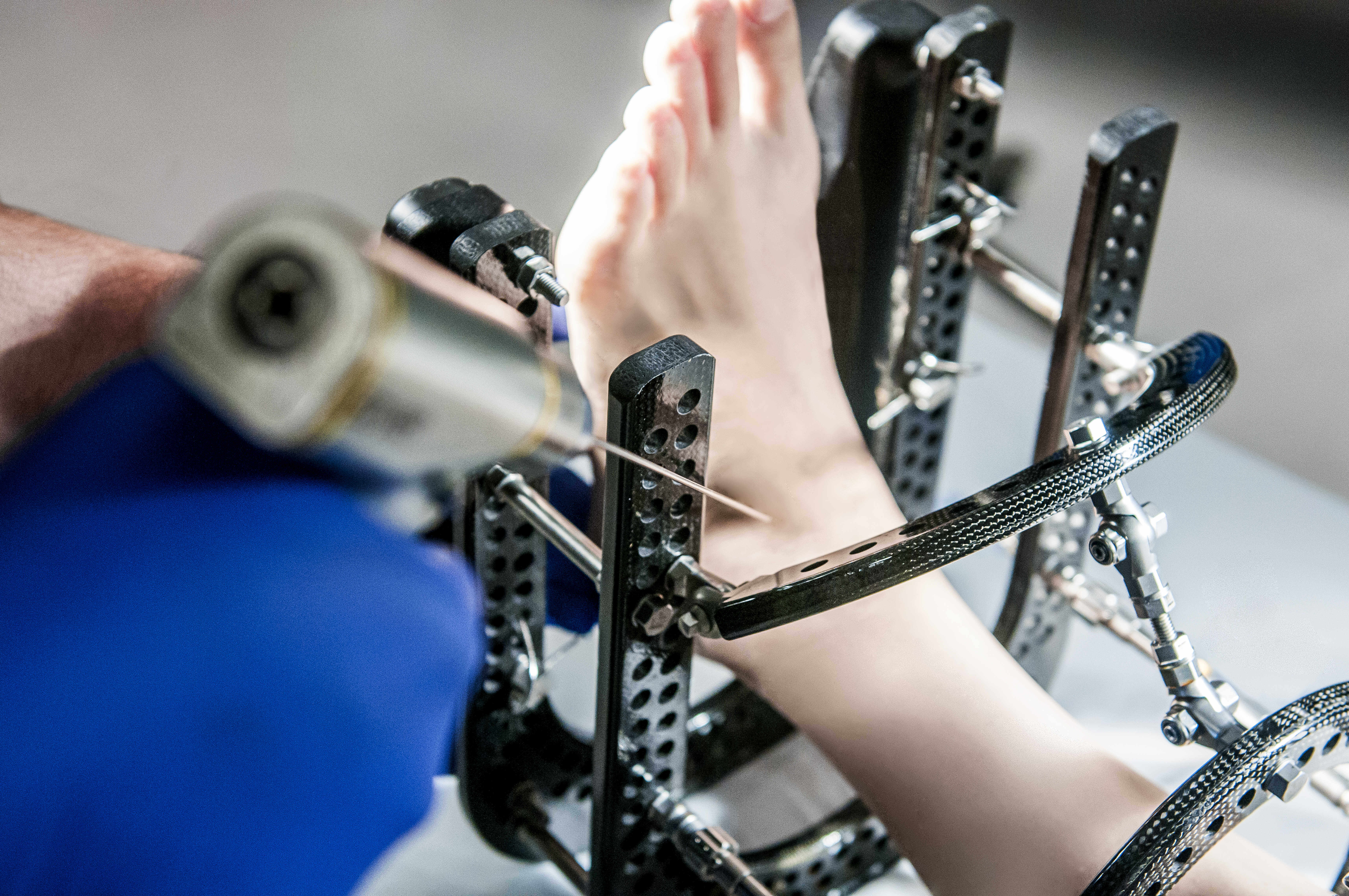
Arthroscopy, also called arthroscopic surgery, is a minimally invasive procedure performed to diagnose and treat joint problems. Ankle arthroscopy is undertaken to evaluate and possibly treat a variety of disorders, such as arthritis in the ankle, an unstable ankle, or bone damage. Among other potential uses for ankle arthroscopy, the surgeon may be able to remove scar tissue, repair cartilage damage, and remove loose pieces of bone or cartilage in the ankle. A major advantage of arthroscopy is the ability to assess and treat conditions without the need to open up the joint using a much larger incision. Because the incisions are small in arthroscopy, tissue damage and scarring is minimized.
After making an incision at the ankle joint, the surgeon:
- Inserts a narrow tube containing a video camera
- Views the ankle joint structure through a video monitor
- Evaluates the condition and, in many cases, treats the problem using additional surgical instruments inserted through the small incision
- In some cases, the surgeon may determine that the severity of the condition calls for fully opening the joint and performing a traditional surgical procedure
Recovery:
Recovery from ankle arthroscopy varies considerably, depending on the severity of the condition and whether the procedure was expanded to traditional open surgery. Generally, recovery from an ankle arthroscopic procedure takes about 2 to 6 weeks and you may have limited weight bearing during this course.