What is Gout? Northridge & Oxnard
Gout is a disorder that results from the build-up of uric acid in the tissues or a joint. It most often affects the joint of the big toe.
Symptoms:
An attack of gout can be miserable, marked by the following symptoms:
- Intense pain that comes on suddenly – often in the middle of the night or upon arising
- Signs of inflammation such as redness, swelling, and warmth over the joint.
Diagnosis:
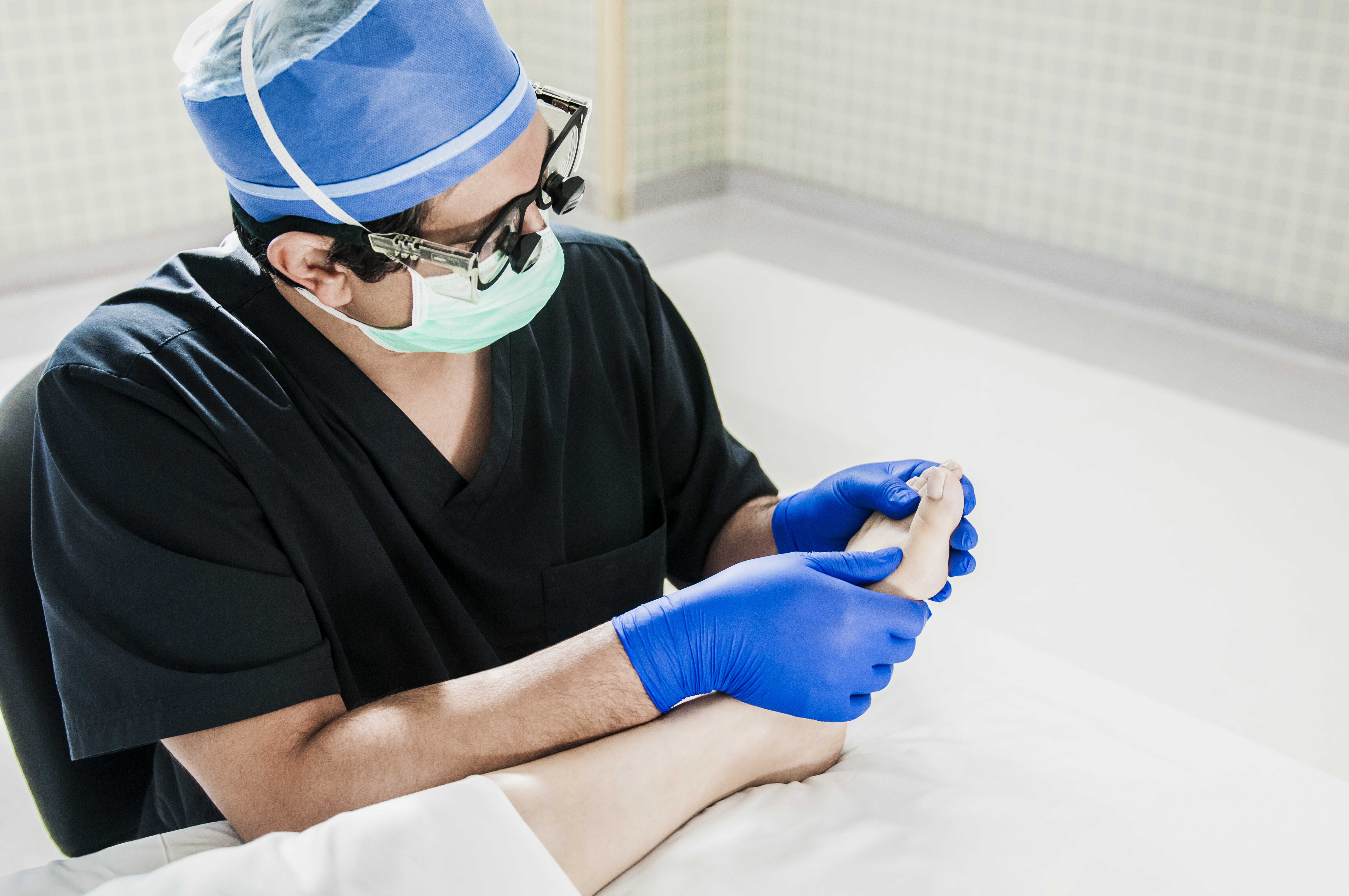
To diagnose gout, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask questions about your personal and family medical history, followed by an examination of the affected joint. Laboratory tests and x-rays are sometimes ordered to determine if the inflammation is caused by something other than gout.
Treatment:
Initial treatment of an attack of gout typically includes the following:
- Medications. Prescription medications or injections are used to treat the pain, swelling, and inflammation.
- Dietary restrictions. Foods and beverages that are high in purines should be avoided, since purines are converted in the body to uric acid.
- Fluids. Drink plenty of water and other fluids each day, while also avoiding alcoholic beverages, which cause dehydration.
- Immobilize and elevate the foot. Avoid standing and walking to give your foot a rest. Also, elevate your foot (level with or slightly above the heart) to help reduce swelling.
The symptoms of gout and the inflammatory process usually resolve in three to ten days with treatment. If gout symptoms continue despite the initial treatment, or if repeated attacks occur, see your primary care physician for maintenance treatment that may involve daily medication. In cases of repeated episodes, the underlying problem must be addressed, as the build-up of uric acid over time can cause arthritic damage to the joint.